
Got questions?
How do I install Ad∙attack?
This is all pretty standard stuff, but please look over these instructions anyway.
First download the installer program from either the link on your invoice, or the link mailed to you when you submitted your trial request.
Most browsers automatically save downloads to a folder called "Downloads". Open that folder or whatever folder you may have saved the downloaded program to.
The setup program is named SetupAA.exe. Locate that file.
We recommend that you right click on that file and select "Run as Administrator" from the displayed popup menu. This will launch the setup program.
Follow the instructions on the screen. When you get to the screen that asks for a serial number, enter the serial number from your invoice. It will look something like this: xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx, with the X's replaced with letters and numbers.
If you are installing the free download, just leave the serial number area blank. You can enter a serial number later if you get one.
Proceed with the installation. At the end, it will ask you if you want to reboot your computer. If you are installing a newer version of Ad-attack over an older version, you must always choose to reboot your computer. If this is a new installation, then reboot is recommended, but not required.
The Ad-attack setup program will put an icon on your desktop. Just click that to enter the program. If the button in the right top area of the program says "Start", then click that to start the program. If it says "Stop", it is already running.
You're good to go!
First download the installer program from either the link on your invoice, or the link mailed to you when you submitted your trial request.
Most browsers automatically save downloads to a folder called "Downloads". Open that folder or whatever folder you may have saved the downloaded program to.
The setup program is named SetupAA.exe. Locate that file.
We recommend that you right click on that file and select "Run as Administrator" from the displayed popup menu. This will launch the setup program.
Follow the instructions on the screen. When you get to the screen that asks for a serial number, enter the serial number from your invoice. It will look something like this: xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx, with the X's replaced with letters and numbers.
If you are installing the free download, just leave the serial number area blank. You can enter a serial number later if you get one.
Proceed with the installation. At the end, it will ask you if you want to reboot your computer. If you are installing a newer version of Ad-attack over an older version, you must always choose to reboot your computer. If this is a new installation, then reboot is recommended, but not required.
The Ad-attack setup program will put an icon on your desktop. Just click that to enter the program. If the button in the right top area of the program says "Start", then click that to start the program. If it says "Stop", it is already running.
You're good to go!
I am not seeing many country names for addresses I access.
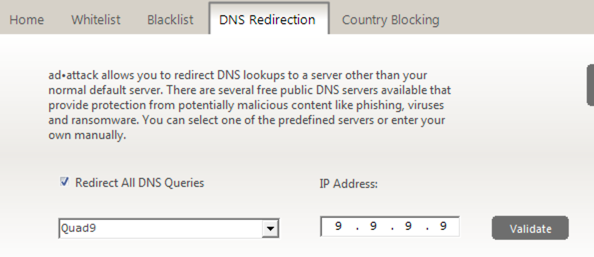
Make sure you redirect your DNS to one of the selections provided in the area shown below.

Do I need to leave the user interface (UI) open?
No you don't. The guts of the program runs as a low level system service. It is running all the time. Whenever the UI is running, the Ad-attack service knows about it and will pipe activity to the screen so you can see what is being blocked or accessed.
How does blacklisting and whitelisting work?
This can be a very powerful feature, and it can be used for more than ad and tracking code blocking.
First, the heart of Ad-attack is our CYBERsitter filter engine that was designed to be extremely powerful, and, intelligent.
For basic white/black listing, just remember that it defaults to "ends with" matching. "Ends with" matching means it looks for a partial domain match that ends with your white/black list term. For example:
Let's say your white or black list term is
That will match any of these:
Alternatively, let's say your white or black list term is
That will match this and not the others:
There are many other powerful ways to add terms including regular expressions. However, they need to be uses in a particular way, so let us know if you have a special need and we'll help you with it.
First, the heart of Ad-attack is our CYBERsitter filter engine that was designed to be extremely powerful, and, intelligent.
For basic white/black listing, just remember that it defaults to "ends with" matching. "Ends with" matching means it looks for a partial domain match that ends with your white/black list term. For example:
Let's say your white or black list term is
mydomain.comThat will match any of these:
abcmydomain.com, www.mydomain.com, abc.mydomain.com.Alternatively, let's say your white or black list term is
www.mydomain.comThat will match this and not the others:
www.mydomain.com,There are many other powerful ways to add terms including regular expressions. However, they need to be uses in a particular way, so let us know if you have a special need and we'll help you with it.
What is DNS redirection?
DNS stands for Domain Name Server. It is like the phonebook for the internet. Getting around the internet requires that computers convert friendly names like google.com to whatever number is assigned to google.com. No one expects you to remember those, so DNS looks them up for you.
Most people use the DNS server assigned to them by their Internet Service Provider. This is usually automatic. But there is no rule that says you have to.
No matter what type of internet activity you are doing, you generate DNS lookups. Some DNS server somewhere sees every website you visit. That means a record is kept of your habits and activity that can be immediately identified as coming from you.
We recommend Quad9 and here's why:
Quad9 does not store any information about your activity. Additionally, they actively block malicious sites to provide a layer of protection against ransomware, phishing, and other types of malware.
You can visit Quad9 and the other optional DNS websites to learn more here:
Quad9: https://www.quad9.net
CleanBrowsing: https://cleanbrowsing.org
CloudFlare: https://www.cloudflare.com/dns/
Google DNS: https://dns.google.com
Most people use the DNS server assigned to them by their Internet Service Provider. This is usually automatic. But there is no rule that says you have to.
No matter what type of internet activity you are doing, you generate DNS lookups. Some DNS server somewhere sees every website you visit. That means a record is kept of your habits and activity that can be immediately identified as coming from you.
We recommend Quad9 and here's why:
Quad9 does not store any information about your activity. Additionally, they actively block malicious sites to provide a layer of protection against ransomware, phishing, and other types of malware.
You can visit Quad9 and the other optional DNS websites to learn more here:
Quad9: https://www.quad9.net
CleanBrowsing: https://cleanbrowsing.org
CloudFlare: https://www.cloudflare.com/dns/
Google DNS: https://dns.google.com
How do I update the blocklists?
This is all handled automatically by a special system service that runs in the background.
Ad-attack updates blocklists in a couple of ways. First, there is the "big" update which updates the entire blocklist. That happens once a week. Secondly, there is a small "delta" update that contains changes since the last big update. This is a very compact and efficient file and is updated every hour.
Although the file is small, the delta file update is very important to ad-attack operation. Occasionally, a big file update will introduce a false positive (something that is blocked in error). The hourly delta update allows us to get fixes out quickly.
Ad-attack updates blocklists in a couple of ways. First, there is the "big" update which updates the entire blocklist. That happens once a week. Secondly, there is a small "delta" update that contains changes since the last big update. This is a very compact and efficient file and is updated every hour.
Although the file is small, the delta file update is very important to ad-attack operation. Occasionally, a big file update will introduce a false positive (something that is blocked in error). The hourly delta update allows us to get fixes out quickly.
How come I see a lot of duplicate BLOCK entries in the UI viewer?
They are actually not duplicates. We only record the domain name of the BLOCK, but the original request was followed by a long string of unintelligible characters. This is sometimes referred to as a token. Each of the entries you see is actually unique, but they are all going to the same domain,
Some sites embed dozens of trackers that load as you scroll the page down. By doing this, they can see what you look at on a page and what items interest you the most by tracking the amount of time you spend before loading the next tracker. Your interests are easily profiled using trackers in this way.
Some sites embed dozens of trackers that load as you scroll the page down. By doing this, they can see what you look at on a page and what items interest you the most by tracking the amount of time you spend before loading the next tracker. Your interests are easily profiled using trackers in this way.
How do I report something blocked improperly?
Use the form on this page and select that subject description from the 'Subject" dropdown. You can also report things you think should be blocked and aren't.
How do I ask questions or get technical support?
Just use the form below and select General technical support as the subject. This will route your message to the tech support ticket system and we'll get back to you as quickly as possible.
27LABS, LLC Terms of Service
27LABS, LLC Privacy Notice